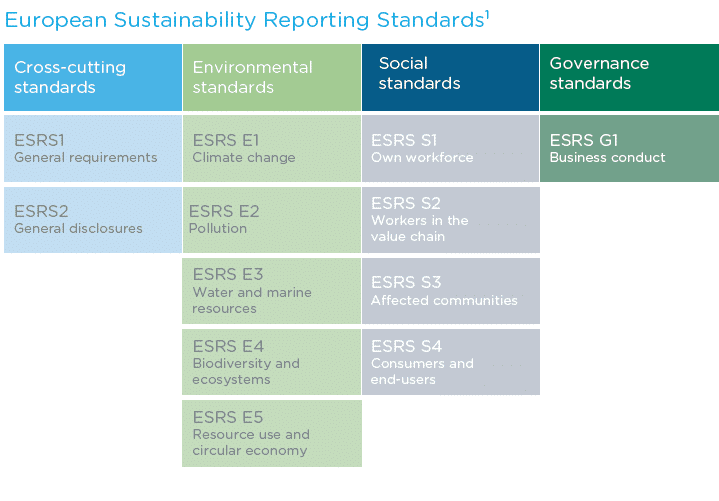
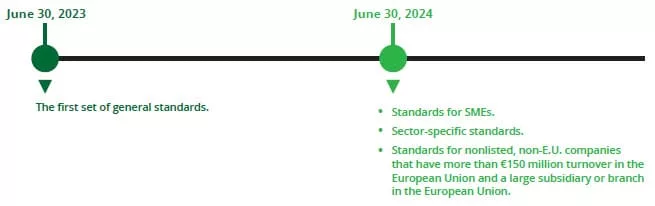
Social responsibility is a key aspect of ESG impact, and it plays a critical role in developing a circular economy. The concept of social responsibility implies that companies have an obligation to act in the best interests of society and the environment. This can take many forms, from reducing carbon emissions to improving working conditions for employees.
One important aspect of social responsibility is the need for companies to engage with stakeholders. This means that companies must consider the concerns and needs of all those who are affected by their operations, including employees, customers, suppliers, and local communities. By doing so, they can build trust and establish themselves as responsible corporate citizens.
Another key element of social responsibility is the need to promote diversity and inclusion. Companies that embrace diversity are more likely to be innovative and successful in the long run. They are also better equipped to navigate complex challenges such as climate change and resource scarcity.
ESG impact also has implications for human rights. Companies must ensure that their operations do not violate basic human rights or contribute to practices such as forced labour or child exploitation. This requires careful monitoring of supply chains and engagement with local communities to ensure that they are not negatively impacted by company activities.
Finally, social responsibility also includes promoting transparency and accountability. Companies must be open about their operations, including their environmental impact and efforts to reduce it. They must also be willing to accept feedback from stakeholders and make changes when necessary.
Social responsibility is a critical component of ESG impact in developing a circular economy. It involves engaging with stakeholders, promoting diversity and inclusion, protecting human rights, promoting transparency and accountability – all while striving towards sustainability goals aimed at minimizing environmental harm through closed-loop systems which reduce waste generation while optimizing resource utilization efficiency throughout product life cycles.
As companies continue to focus on these aspects of ESG impact alongside economic performance metrics (such as profits), they will create sustainable value for themselves while contributing positively towards society’s goals for a more circular economy.